- Java RMI is a method which helps you to run applications which are located in remote server. "simply said you can run a system which is not in your computer may be friends computer using this method".
- May be hackers might do this this things,they can install a application in your computer and they can control your computer using this method.
- In both machines JVM is required. No way you can run java without JVM, so this is a must.
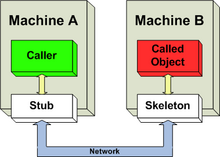
- Oldest method to implement this was stub skeleton model.
- Stub and skeleton are like proxies or intermediary part which convert method definitions variable method calls etc. to byte streams.
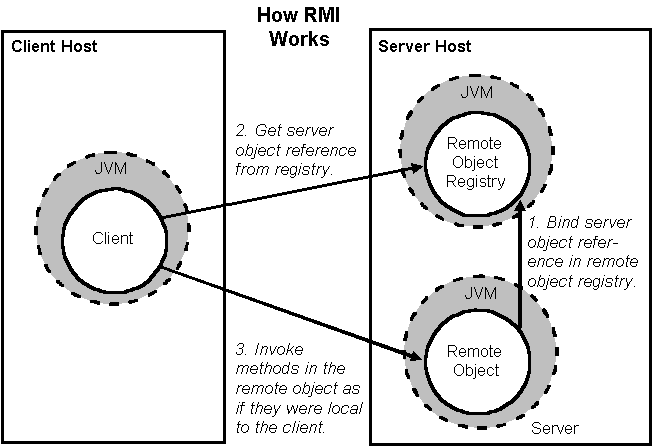
1.Client requests for the remote object
reference to naming service
2.Once the naming service locates the
server host, RMI registry provides a stub (proxy) of remote object.
3.Client can make call using the stub
4.Basically, the request from the stub is
sent to the server skeleton which makes the actual request to the remote
object.
5.Similarly, the server response is sent
back through skeleton and stub to the client.
- Java implementation of this is as follows,
- Make a Remote Interface
- an interface extending java Remote class
- for both client and server.
- In "server" class, in this context implements the interface,creates an instance of the remote object implementation, exports the remote object, and then binds that instance to a name in a Java RMI registry
- Implement client
- This is an implementation of Temperature monitor application using RMI, here temperature values are randomly simulated using an algorithm.
- Remote Interface of server
/*TemperatureSensor interface extending remote interface this can be called from remote JVM*/
interface TemperatureSensor extends java.rmi.Remote
{
public double getTemperature() throws //get temperature from the server
java.rmi.RemoteException;
public void addTemperatureListener // add a listner to listner list
(TemperatureListener listener )
throws java.rmi.RemoteException;
public void removeTemperatureListener //remove listner from the list
(TemperatureListener listener )
throws java.rmi.RemoteException;
}
- Remote Interface of Client
/* Listner interface extending remote interface this can be called from remote JVM*/
interface TemperatureListener extends java.rmi.Remote
{
/*this is the callback function which server calls upon a change in temperature*/
public void temperatureChanged(double temperature) throws java.rmi.RemoteException;
}
- Implementation of the server
import java.util.*;
import java.rmi.*;
import java.rmi.server.*;
/* implements the TemperatureSensor interface
Used for exporting a remote object with JRMP and obtaining a stub that communicates to the remote object
and a seperate thread for the server*/
public class TemperatureSensorServer extends UnicastRemoteObject implements
TemperatureSensor, Runnable {
private volatile double temp;
private ArrayList<TemperatureListener> list = new ArrayList<TemperatureListener>();
//contructor initiate temperature to 98;
public TemperatureSensorServer() throws java.rmi.RemoteException {
temp = 98.0;
}
//return the current temperature
public double getTemperature() throws java.rmi.RemoteException {
return temp;
}
//adds a TemperatureListener object to the list of listners
public void addTemperatureListener(TemperatureListener listener)
throws java.rmi.RemoteException {
System.out.println("adding listener -" + listener);
list.add(listener);
}
//remove a TemperatureListener from the list of listners
public void removeTemperatureListener(TemperatureListener listener)
throws java.rmi.RemoteException {
System.out.println("removing listener -" + listener);
list.remove(listener);
}
public void run() {
Random r = new Random();
for (;;) {
try {
// Sleep for a random amount of time
int duration = r.nextInt() % 10000 + 200;
// Check to see if negative, if so, reverse
if (duration < 0) {
duration = duration * -1;
Thread.sleep(duration);
}
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
}
// Get a number, to see if temp goes up or down
int num = r.nextInt();
if (num < 0) {
temp += 0.5;
} else {
temp -= 0.5;
}
// Notify registered listeners
try{
System.out.println(String.valueOf(temp));
notifyListeners();
}
catch(Exception e){
}
}
}
private void notifyListeners() {
// TO DO: Notify every listener in the registered list if there is a change in the temperature
for (TemperatureListener tl : list) {
try{
double temperature=getTemperature();
tl.temperatureChanged(temperature);
}
catch(Exception e){
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Loading temperature service");
try {
//bind TemperatureSensorServer to RMI registry from which the client can get a reference of service
TemperatureSensorServer sensor = new TemperatureSensorServer();
String registry = "localhost";
String registration = "rmi://" + registry + "/TemperatureSensor";
Naming.rebind(registration, sensor);
Thread thread = new Thread(sensor);
thread.start();
} catch (RemoteException re) {
System.err.println("Remote Error - " + re);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Error - " + e);
}
}
}
- Then the client implementation
import java.rmi.*;
import java.rmi.server.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.io.Serializable;
/*this class implements the TemperatureListner interface
Used for exporting a remote object with JRMP and obtaining a stub that communicates to the remote object and a sperate thread for each client*/
public class TemperatureMonitor extends UnicastRemoteObject implements
TemperatureListener, Runnable,Serializable {
private int count = 0;
public TemperatureMonitor() throws RemoteException {
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
String registration = "//localhost/TemperatureSensor";
//lookup for the interface object in RMI registry and get the reference to the object
Remote remoteService = Naming.lookup(registration);
TemperatureSensor sensor = (TemperatureSensor) remoteService;
double reading = sensor.getTemperature();
System.out.println("Original temp : " + reading);
TemperatureMonitor monitor = new TemperatureMonitor();
// Add method call to register the listener in the server object
sensor.addTemperatureListener(monitor);
monitor.run();
} catch (MalformedURLException mue) {
} catch (RemoteException re) {
} catch (NotBoundException nbe) {
}
}
//callback function invoked by TemperatureSensorServer to notifiy temperature change
public void temperatureChanged(double temperature)
throws java.rmi.RemoteException {
System.out.println("\nTemperature change event : " + temperature);
count = 0;
}
//TemperatureMonitor thread counting until a temperature change occur
public void run() {
for (;;) {
count++;
// note that this might only work on windows console
System.out.print("\r" + count);
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
}
}
}
}
- to run this first set class path of your working directory using command prompt
set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;<<your directory path here>>
- Generate the server and client stub using the command ‘rmic classname'
- Start the rmiregistry using the command ‘start rmiregistry’.
- java –Djava.security.poicy=allowall.policy 'classname'